The risk premium on a conventional rate does not change during the loan's duration. Once a mortgage has been "locked in," it will not modify regardless of price fluctuations. Fix-rate mortgages are popular among borrowers who value stability and want to keep their homes for a long time. Most mortgages with a fixed interest rate are amortizing loans. Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) are an alternative to fixed-rate mortgages since their interest rates fluctuate. For the duration of the loan term, the cost of borrowing on a "fixed-rate mortgage" will not change. This implies the interest rate mostly on the mortgage will remain the same throughout its duration. Customers who like to budget their money regularly often choose mortgages with fixed interest rates.
The Workings Of A Fixed-Rate Mortgage
Despite the wide variety of mortgages, they can all be broken down into two broad classes: adjustable-rate and fixed-rate mortgages. The interest rate on a variable-rate loan is initially fixed but changes over time relative to a predetermined index. However, the interest rate on something like a fixed-rate mortgage does not change during the length of the loan's life. Fixed-rate mortgage payments do not change in response to market fluctuations like adjustable- and variable-rate mortgages. A fixed-rate mortgage is one in which the interest rate will not change regardless of whether or not the prime lending rate changes. Somewhere between fixed- but instead variable-rate loans lies the customizable mortgage (ARM). Typically, an interest rate is set for an initial term that spans many years. As time goes on, the interest rate will change regularly, maybe once a year or even monthly.
Terms Of Fixed-Rate Mortgages
The mortgage term refers to the total amount of time you will be required to make payments on the loan. Mortgages with a fixed interest rate in the United States often have periods of 10, 15, 20, or 30 years. The 30-year period is the most common choice, followed by the 15-year tenure.
How Long Does A Fixed-Rate Mortgage Take To Pay Off?
Your mortgage repayment period will be set at the start of your loan. A 30-year fixed-rate mortgage, the most typical kind, gives you three decades to make monthly payments on your loan. Although it seems like a lot, spreading your payments over a longer period might help you save money and make more space in your budget. The 15-year traditional payment is yet another popular choice. While the interest rate may be lower, the repayment period may be cut in half. Borrowers who can afford it and want to pay off their property quicker and with less interest may consider a 15-year fixed-rate mortgage.
How To Figure Out The Cost Of A Fixed-Rate Mortgage
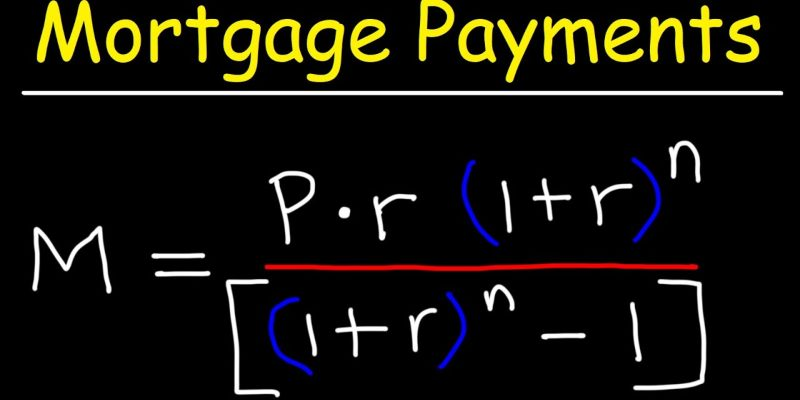
Borrowers with fixed-rate mortgages pay different amounts of interest throughout the life of the loan, called the amortization period. Your mortgage's borrowing cost and quarterly payment amount will remain the same, but the mortgage's terms will change. Mortgage holders initially put a larger portion of their payments towards the interest on their loans. Still, as they go through the repayment process, they put a greater portion of their payments forward toward the loan principal. As a result, the mortgage term is relevant for figuring out how much a mortgage will cost. As a general rule, interest rates are higher for lengthier loan terms. The interest rate on a mortgage with a 15-year term is lower than that on a 30-year mortgage with the same principal amount. It's not always easy to crunch the numbers to calculate the precise monthly payment on a fixed-rate mortgage.
Conclusion
Mortgage loans with an interest rate set at the time of loan origination and do not fluctuate over the loan's duration are called fixed-rate mortgages. Borrowers are safeguarded against interest rate increases with a fixed-rate mortgage, and consistent monthly payments facilitate planning and budgeting. There is a correlation between a borrower's credit score and the length of the fixed-rate mortgage term. Regarding home loans, the fixed-rate mortgage is a top choice. The interest rate on a fixed-rate mortgage doesn't change over the loan's duration. In contrast, the interest rate on a fixed-rate mortgage never changes, unlike a variable-rate mortgage. A fixed-rate mortgage might be a good option if you want a stable monthly payment and are comfortable sticking to a strict budget.







